4. Integration by Parts
Recall:
\(\displaystyle \int u\,dv=u\,v-\int v\,du\) where
\(du=\dfrac{du}{dx}\,dx\) and \(dv=\dfrac{dv}{dx}\,dx\)
For definite integrals:
\(\displaystyle \int_a^b u\,dv=\left[\rule{0pt}{10pt}u\,v\right]_a^b-\int_a^b v\,du\)
Homework
-
\(\displaystyle \int x\cos(2x)\,dx\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int \dfrac{3x+1}{e^{2x-1}}\,dx\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int x^2e^{4x}\,dx\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int (x^3+3x^2)\sin 3x\,dx\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int x(x-2)^3\,dx\) Compute once by parts and once by substitution. Check they give the same answer.
-
\(\displaystyle \int y^3\cos(y^2)\,dy\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int (3p^2+2p)\ln p\,dp\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int x\,\text{arcsec}\,x\,dx\) for \(x \ge 1\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int \ln(x^3)\,dx\)
-
An important function in physics is the sine integral defined by \[ \mathrm{Si}(x)=\int_0^x \dfrac{\sin t}{t}\,dt \] There is no exact formula for the result of this integral; it must be computed numerically. However, its derivative is easily found by the fundamental theorem of calculus: \[ \dfrac{d}{dx}\mathrm{Si}(x) =\dfrac{\sin x}{x} \] In addition, its antiderivative is easily found by integration by parts.
Compute \(\displaystyle \int \mathrm{Si}(x)\,dx\). -
\(\displaystyle \int_0^2 2x^2e^{2x}\,dx\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int_1^3 x^2\ln x\,dx\)
-
Sketch the region bounded by the curves \(y=\ln x\), \(y=-\ln x\) and \(x=e\). Then find the area of the region.
-
Find the average value of the function \(f(x)=x e^{-x}\) over the interval \([0,2]\).
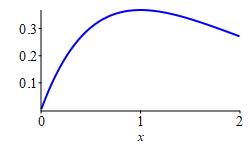
-
\(\displaystyle \int e^{3x}\cos(4x)\,dx\)
-
\(\displaystyle \int_0^{\pi/2} \sin(3x)\cos(4x)\,dx\)
-
Use the the sine reduction formula: \[ \int \sin^n x\,dx =-\,\dfrac{1}{n}\sin^{n-1}x\cos x+\dfrac{n-1}{n}\int \sin^{n-2}x\,dx \] Compute \(\displaystyle \int \sin^3 x\,dx\).
-
Find the area of the region below \(y=x\cos x\) above the \(x\)-axis between \(x=0\) to \(x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}\).
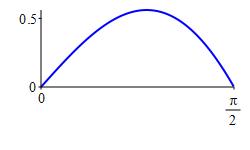
Use integration by parts to compute the following indefinite integrals. Be sure to check your answer by differentiating.
Use integration by parts to compute the following definite integrals. Be sure to check your indefinite integral by differentiating.
Use integration by parts to compute the following indefinite integrals. Be sure to check your answer by differentiating.
Heading
Placeholder text: Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum Lorem ipsum